Residual Stresses and Distortions in Modern Manufacturing (3 Credits)
Fall 2020
Course Description
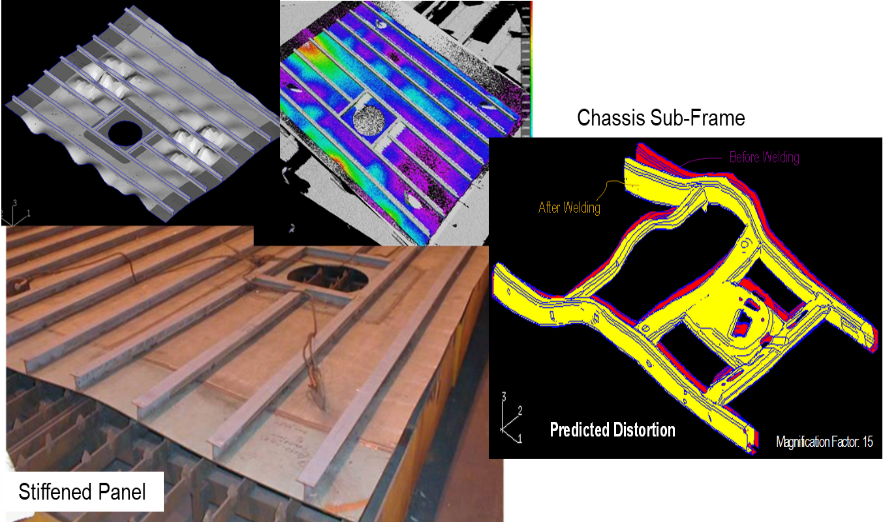
This course starts with an introduction to some of the challenges in the manufacture of modern metallic structures to meet increasingly stringent structural lightweighting and performance requirements. Residual stresses and distortions caused by modern manufacturing processes, such as laser forming, thermal cutting, solid-state joining, arc welding, as well as “3D printing” have become increasingly a concern both for dimensional accuracy control in modular construction and for ensuring construction quality as well as structural integrity. This new course will introduce a series of novel first-principle based approaches to solving residual stress and distortion problems associated with these manufacturing processes. Basic finite element (FE) modeling procedures will also be discussed with application-oriented examples. plate/sheet processing, thermal cutting, welding, friction-stir, and rapid metal deposition processes. Real-world examples (aerospace, automotive, and shipbuilding) will be used to demonstrate the problem-solving process and effective mitigation techniques.
Course Topics
- Modern manufacturing challenges
- Material behaviors in thermal manufacturing
- Basic thermoplasticity descriptions (1D modeling)
- Temperature-dependent stress-strain relation
- Localized thermomechanical behaviors
- 1-bar model
- 3-bar model
- n-bar model
- Reduced-order modeling methods
- Shrinkage force method (analytical)
- Shrinkage strain method (numerical)
- Applications:
- Plate/sheet processing
- Thermal cutting/thermal forming (e.g., line heating)
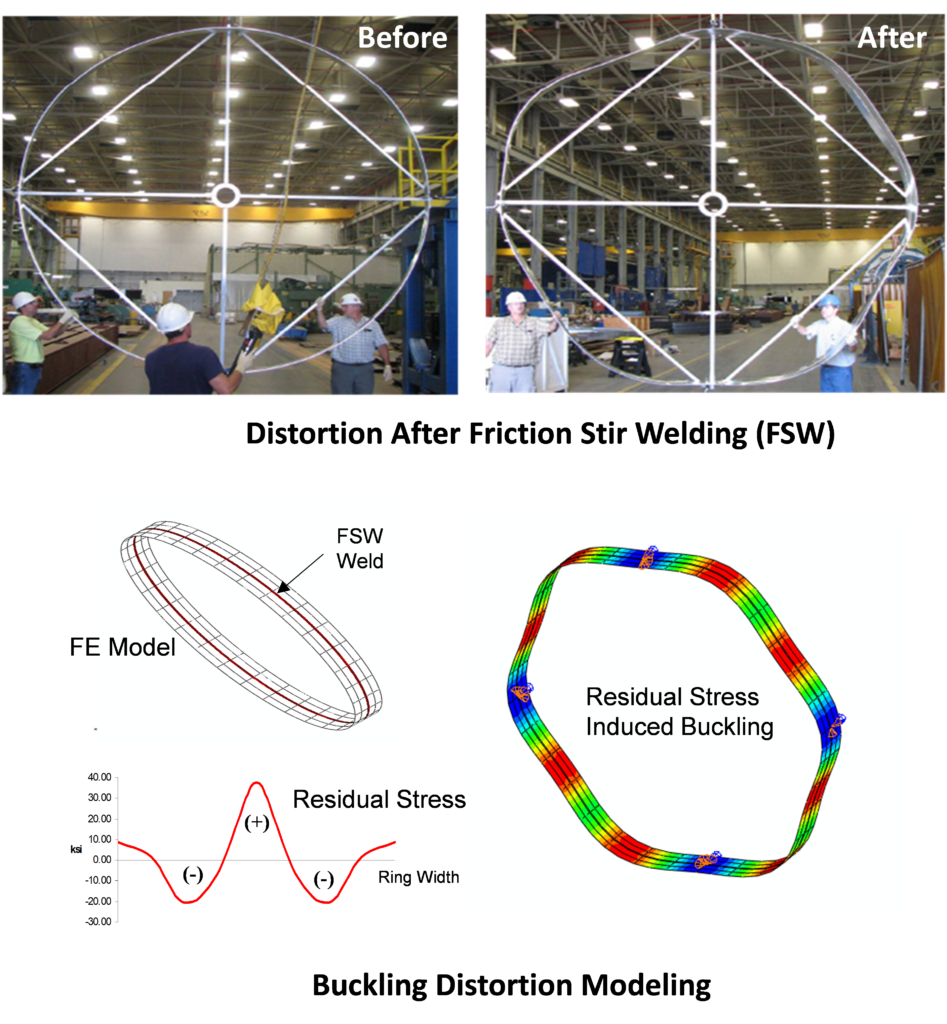
- Welding/joining including friction stir welding and surface processing
- Metal additive manufacturing (“3D printing”)
- Basic FE modeling procedures
- Treatment of moving heat source
- Plastic zone determination
- Residual stress estimate
- Stable and unstable distortion modeling
- Principles for residual stress and distortion control
- Various industrial examples and problem-solving demonstrations
Grading
Homeworks (6~7): 40%
Two quizzes: 60%